(Click here to read our disclaimer)
Letrozole is an aromatase inhibitor that may have benefits in managing hormonally-responsive breast cancer in animals. In scientific studies it has been indicated that letrozole may be used for ovarian stimulation because it has fewer side effects than Clomiphene Citrate and fewer changes of causing multiple gestation. Some studies indicate that letrozole may have a lower risk of birth defects in lab rats than chemicals applied for similar purposes.
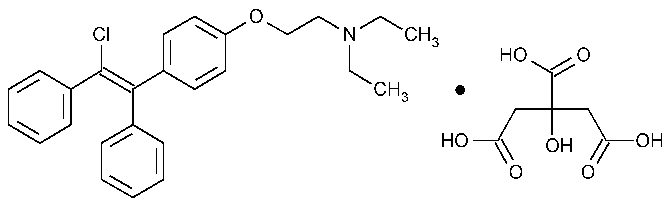 Studies have also focused on letrozole as a potential option to address gynecomasstia if this disease is in the early stages of treatment, as well as a potential way to manage spermatogenesis.
Studies have also focused on letrozole as a potential option to address gynecomasstia if this disease is in the early stages of treatment, as well as a potential way to manage spermatogenesis.
However, it is important to note that this chemical should not be used outside of a scientific setting and is not yet approved for use on humans or studies on humans.
Influence on Complexation and Hydroxybutenyl-beta Cyclodextrin
- This study worked to examine the in-vitro effects of three various CDs on the chemical letrozole because this chemical is insoluble in water.
- This study indicated that the most promising chemical, hydroxybutenyl-beta cyclodextrin could be used in-vivo in both male and female rats in spite of the fact that letrozole has dramatic gender-based difference when applied as a pharmacokinetic.
- The terminal half-life of the chemical letrozole in male rats is 11.5 while it is 42.3 in female rats.
- Creating a more complex chemical by combining letroxole with the HBenbetaCD helps to improve oral absorption in male rat subjects and helped to maximize the abortion in female rat subjects. In both genders, the presence of HBenbeta CD helped to improve in-vivo rates of absorbtion.
When letrozole was applied in the rat test subjects in capsule form the HBenbetaCD, presence resulted in a higher absolute oral bioavailability. This implies that the solubility limits in the extent and rate of letrozole absorption exist for male rats, but are not limited in the rate of absorption for female rats.
Induced Polycystic Ovaries in the Rat
- This study attempted to develop new models in animals for the study of what’s known as polycystic ovaries by using aromatase inhibitor letrozole(non-steroidal).
- Thirty-four rats were taken as subjects and divided into a control group and three test groups of 10 rats each. Each of these treatment groups were given concentrations of letrozole in .1, .5 and 1 mg respectively. The chemical was administered to the rats once a day for 21 days.
- Throughout the testing period, the rats were collected for vaginal spears and estrus cycle determination. On the subsequent day letrozole administrations, the rats were killed and the ovaries and uteri were weighed and excised while serum hormone levels in the ovaries were examined.
- Compared to the rats in the control group, the ovaries in the study groups had a higher incidence of subcapsular ovarian cysts with capsular thickening with incomplete luteinization. A decreased number of corporea lutea was also seen.
These results are not fully convincing in the study of polycystic ovaries or PCOS. However, this is a vital step in developing an animal model that could be used to study polycystic ovary syndrome in humans without the need for human test subjects.
Letrozole is still in the testing phase. There are no approved doses or applications of this chemical that are approved for use in humans or outside of a research setting.
Sources:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17637172
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15010188
Click here to view our entire PDF research library
Click here to view/download the PDF version of this article