(Click here to read our disclaimer)
Obesity can interfere with the function of organs such as the pituitary gland or pancreas. If these organs cannot receive the proper messages then the system will fail to produce proper levels of chemicals, such as insulin.
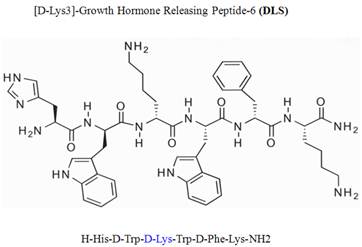
Studies are undergoing to determine the effectiveness of using artificial hormones to help regulate these hormone levels. The growth chemical GHRP6 is currently being studied for such a purpose, though it will take some time before any coherent results are determined.
Natural Interactions with Insulin
 Natural hormones are designed to stimulate a variety of chemicals to encourage the tissue cells to multiply.
Natural hormones are designed to stimulate a variety of chemicals to encourage the tissue cells to multiply.
- Hormones are designed to stimulate the pituitary or other glands or what’s secreted from these glands to stimulate tissue. GHRP6 is a chemical that has been designed to mimic the properties of the latter group.
- Different types of hormones are intended to stimulate different types of tissue. This may include stimulating bone knitting or muscle production.
- Some natural hormones will also stimulate the pancreas. If these hormones are not functioning properly it can result in excessive growth that may result in obesity.
It is important to note that artificial hormones such as GHRP6 do not function in the same manner as the natural hormones they are designed to mimic.
In tests on rats it has been shown that chemicals such as GHRP6 remain in the system much longer than hormones which naturally occur in the system. The impact this added time in the system has on the tissues is not yet known.
Impact of GHRP6 on Hypopituitary and Obese Conditions
Scientists have determined that a low reproducibility rate of hormones may increase the risk of obesity.
- To determine the full effects of these hormones, a variety of mice subjects including males and females were studied. Groups included those that were obese, obese but otherwise healthy, those that suffered from hypopituitarism and those with a normal body-mass and health rates. These subjects were checked using a radioimmunoassay to determine the natural hormone rates in their system.
- The study concluded that those mice suffering from hypo-pituitarism, specifically those that were already obese, saw a significant dip in their natural hormones. Those that did not suffer from hypopituitarism or those with a normal body mass index did not see this response.
GHRP6 and acipimox were offered as a potential treatment option to correct these levels in the mice that saw a hormone decrease.
The conclusions showed that doses of acipimox or GHRP6 were not effective in restoring the natural hormone levels necessary to overcome hypopituitarism. However, a combination of the natural GHRH and GHRP6 saw fewer side effects than the other doses.
Additional research will be necessary to determine the safety or full effectiveness of artificial hormones in treating organic conditions.
Click here to view the homepage of our store
Click here to view our entire PDF research library
Click here to view or download this article in PDF format