(Click here to read our disclaimer)
(Click here to buy Levothyroxine T4 from our store)
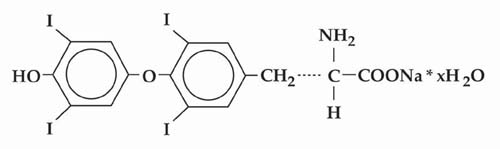
Levothyroxine T4 refers to a synthetic chemical that mimics the natural chemical thyroxine. Thyroxine is secreted by the follicular cells within the thyroid. Scientists are attempting to perfect an artificial version of this hormone as a means of treating thyroid deficiencies or cancers in animals in the future.
Currently, research into the development of levothyroxine T4 largely focuses on addressing the symptoms of hypothyroidism. Some studies have implied that this chemical could be used to manage goiter because it has been shown to lower the presence of thyroid-stimulating hormone in animal subjects.
However, the application of this chemical must be taken with care as test subjects that were exposed to this chemical long-term showed a variety of negative side effects including decreases in bone mineral density.
Effects on Hypothyroidism on the Testes of Mature Rats
The study hoped to investigate the effects of propylthiouracil (PTU) on rat testes compared to the treatment regimens of zinc and levothyroxine.
- A group of 20 sexually mature albino rats were exposed to PTU for two weeks to make the subjects hypothyroidism.
- The effects of PTU on the testicular function were studied using histopathological methods after the unilateral orchiectomy performed on day 15 of the study. Treatments were evaluated using serum thyroid-stimulating hormone and the zinc levels on the first day, after one week and on day 15.
- After this administration, the rats were divided into five groups that would be given lr3 igf1 or zinc for a total of 15 days.
Those treated with levothyroxine saw a decreased tubular diameter, thickening of the basal membrane and interstitial oedema in the hypothyroidic testicles. After the treatment was completed the testicular histology and the spermatogenesis would gradually recover in all of the groups that were given hypothyroidism.
Those that were given a combination of levothyroxine and zinc sulphate saw the greatest increase in improvement levels, which implies that zinc may have an effect on testicular function.
Effect on Rat Skeletal Muscle Resistance Arteries
This study investigates the idea that hormones would have vasodilatory effects on the body of the subjects and attempts to determine if such effects would be endothelium-dependent.
- Skeletal muscle in rats and the resistance arteries of around 100 microns were dissected to measure the vessel diameter changes by using a video-detection system.
- Each vessel was then pre-constricted using thromboxane to measure the percentage of dilation after the exposure of increasing concentrations of levothyroxine or triiodothyronine. Dialation in response to triiodothyronine was measured after the endothelial denudation.
- The measurements indicated that triiodothyronine had a greater effect on the rat test subjects than levothyroxine.
These results indicate that thyroid hormones cause direct vasodilatory effects in body endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent components. These results imply that that these hormones can have direct vasodilatory effects which can partially account for the cardiovascular actions these hormones have when a rat has hyperthyroidism or when the chemicals were administered pharmacologically during cardiac surgery.
Given the current risk of side effects associated with the application of levothyroxine T4 in animal test subjects, this chemical is not yet approved for use in human subjects or in a clinical setting.
Sources:
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com
http://www.anesthesia-analgesia.org/content/85/4/734.short
Click here to view our entire PDF research library
Click here to view/download the PDF version of this article